PMBOK
The PMBOK Guide is process-based, meaning it describes work as being accomplished by processes. This approach is consistent with other management standards such as ISO 9000 and the Software Engineering Institute's CMMI. Processes overlap and interact throughout a project or its various phases. Processes are described in terms of:
- Inputs (documents, plans, designs, etc.)
- Tools and Techniques (mechanisms applied to inputs)
- Outputs (documents, products, etc.)
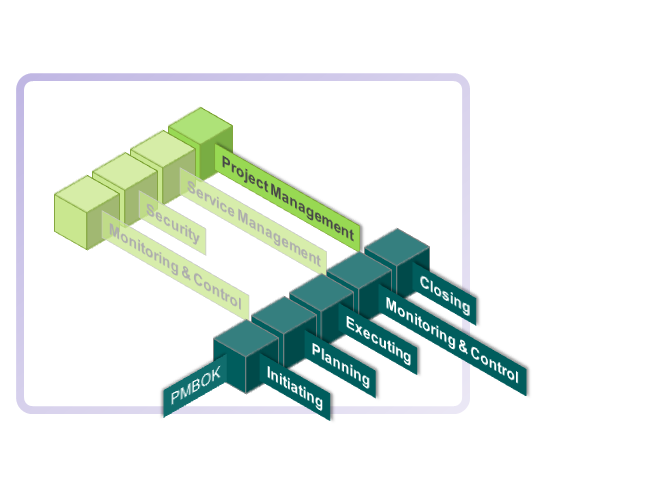
The Guide recognises 42 processes that fall into five basic process groups and nine knowledge areas that are typical of almost all projects.
The five process groups are:
- Initiating
- Planning
- Executing
- Monitoring and Controlling
- Closing
The nine knowledge areas are:
- Project Integration Management
- Project Scope Management
- Project Time Management
- Project Cost Management
- Project Quality Management
- Project Human Resource Management
- Project Communications Management
- Project Risk Management
- Project Procurement Management
Each of the nine knowledge areas contains the processes that need to be accomplished within its discipline in order to achieve an effective project management program.
Each of these processes also falls into one of the five basic process groups, creating a matrix structure such that every process can be related to one knowledge area and one process group.
From an Enterprise Architecture perspective, Project Management is a specialist discipline for implementing a new architecture or for introducing a significant variation to an existing architecture that has been initiated in the Enterprise Architecture practice. The scope of a project is determined by the architecture.
Using the context of an ongoing Enterprise Architecture practice within an organisation, services ideally will be managed in an ongoing manner and in accordance with a defined Service Management methodology such as ITIL. New services and variations to services are introduced via a Design phase as the responsibility of an Enterprise Architecture practice. These architectures are implemented at a Transition phase in accordance with a Change Management process to validate changes and introduce them in a controlled manner and this is the function of Project Management. Multiple, concurrent changes may be dealt with as a Program comprised of multiple projects.
Alternatively however, a project may include architecture as one part of a wider scope. Where large scale and long term projects are undertaken involving a range of ICT domains, a Project / Program Management Office (PMO) may include an Enterprise Architecture and engineering practices.
Using the TOGAF Architecture Development Method as the reference, Project Management would contribute to the core Requirements Management and so form a sub-set of the EA framework.
Requirements Management would align with the Change Management processes in Service Management in accordance with common strategic business objectives and being undertaken in a controlled manner within a common ICT governance arrangement where the respective stakeholders such as Enterprise Architects, Project Managers and Change Managers would be participants in assessing and planning for change via entities such as Architecture Boards and Change Advisory Boards wherein Architecture Principles provide a primary means of assessing changes.
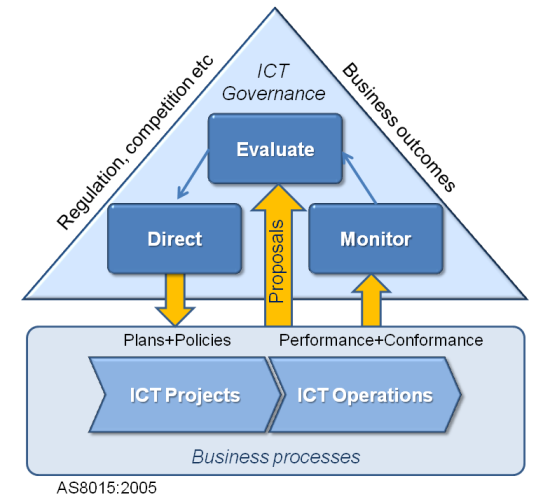
Corporate governance of information and communication technology standrad AS8015:2005 provides guiding principles for an organisations' owners, board members, directors, partners, senior executives, or similar on the effective, efficient, and acceptable use of Information and Communication Technology (ICT) within their organisation. The Standard applies to the governance of resources used to provide information and communication services to an organisation. These guidelines provide for effective alignment of activities across architecture, projects and services.